Developer Mode Survey Editability
Description
Determine with customized rules whether a submitted survey can be edited using custom Javascript code scripts. Programming custom logic is an alternative to the yes or no options for determining a survey's editability after submission. For example, you can set a survey to be editable when found within a specific task state or priority; otherwise, it could be set to read-only.
This feature is useful when submitted forms affect task characteristics or contain information that should not be modified.
The code is inserted in the survey's settings panel in the Access section.
By default, surveys are not editable, except for surveys created before the release of this feature (June 2022).
If a submitted survey form is part of a routine, even if it is edited, the data gathered by the routine remains the same.
Setup
To enable the use of custom code to determine survey editability:
- Select the Administrator on the Main Menu Bar.
- From the Administrative Panel, choose Surveys.
- In the Form table, choose to edit the survey you wish to customize to open the survey's settings panel.

- In the Editable field, choose Developer Mode.
- Select the context.
- Place the code script in the function field.
Configuration details and code guidelines are explained below. Code examples and expected results are shown further below.
See the Embedded Code Editor section for more information on how to use the editor.
Coding Guide
Code used for determining survey editability should follow the guidelines specified below.
Context
The context field indicates a relevant source from which data can be extracted. Sources are Cotalker objects structured with a corresponding data model. The context can be used as a variable representing the object within the code to extract data from an indicated source.
- Currently, only the
channel#taskcontext is available. This context permits retrieving data from the task channel associated with the survey. - The
channel#taskcontext can be used as a variable that allows your code to access the task's data. - The task's data is structured according to the COTTask data model.
Function
Consider the following guidelines for the code to be used:
- The code must be a function written in Javascript. The function must be named
runwithout any arguments. - The function must return a Read-only command array.
- The code must include the context as a variable in your code if you wish to retrieve data from the available contexts.
Structure Example
function run() {
/* yourCode; */
return [{
cmd: 'SET_READONLY',
value: true | false
}];
}
Example
Below is an example of a code script and how it affects end-users. This code follows three simple steps to determine survey editability.
- The code first checks if a task is present in the channel. Even though there is no task, a command array must be returned, so the function returns a false read-only value.
- If the task is in a specific state, it returns a false read-only value. The survey can be edited.
- If the task is in any other state, a read-only value is returned, and the survey cannot be edited.
- In this example, we use the
taskvariable, that represents the context source, to retrieve the task's current state. - By looking at the task's data model, we know that we can find this information through
task.status. The information retrieved is an ObjectId which identifies the task. - We must also get the ObjectId of the state in which the survey could be edited.
- An
ifstatement is used to compare both ObjectIds.
Code Samples
function run() {
const task = context['channel#task']; // The context used as a variable permits extracting specific data from the object represented.
console.log('Check survey editability.');
if (!task) {
console.log('No task present.');
return [{ //Command array that must be returned.
cmd: 'SET_READONLY',
value: false
}, ]
} else if (task.status === "604bb9d827f6ba0008435eac") { // task.status retrieves the task's current state. The number to be equaled is the ObjectId of the state in which surveys can be edited.
console.log('Survey is editable.');
return [{ //Command array that must be returned.
cmd: 'SET_READONLY',
value: false
}, ]
} else {
console.log('Survey is not editable.');
return [{ // Command array that must be returned.
cmd: 'SET_READONLY',
value: true
}, ]
}
}
Expected Results
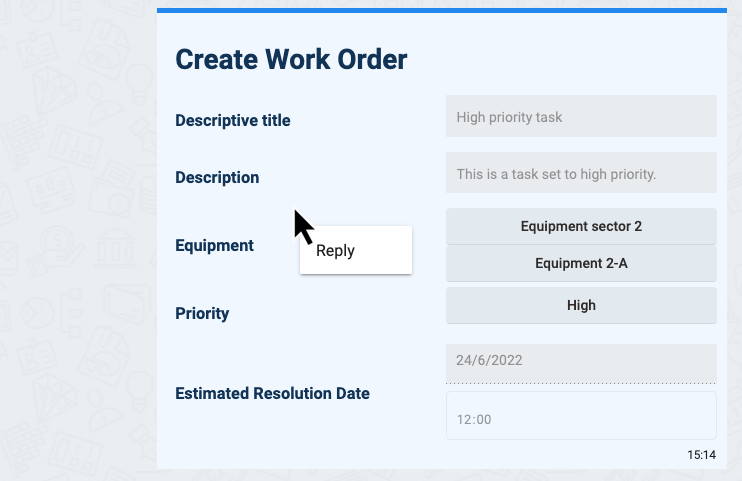
Below is an example of a survey following the logic expressed in the code used above.
This survey finds itself in a task state which allows editing:
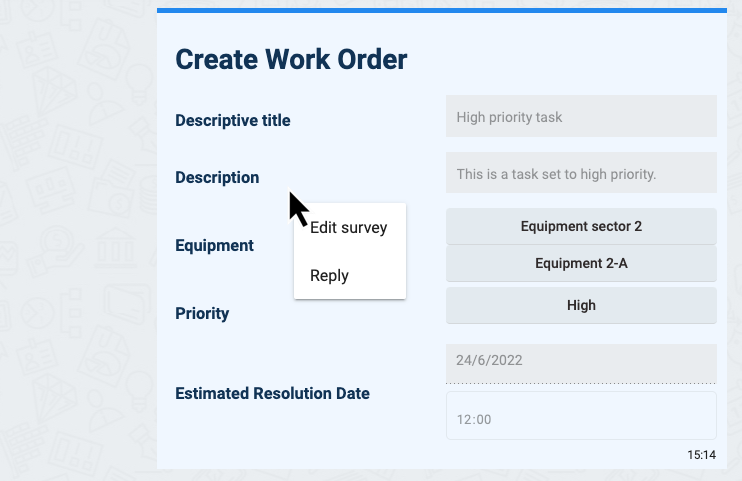
The task state has changed and now the survey cannot be edited: